Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body is unable to produce or use insulin effectively, leading to high blood sugar levels. Diabetes can have serious health consequences, including heart disease, kidney failure, and blindness. However, with proper management, people with diabetes can live long and healthy lives. In this article, we will explore practical strategies for living well with diabetes.
Understanding Diabetes and Its Impact on Health
 Diabetes is a condition in which the body is unable to produce or use insulin effectively. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes occurs when the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough insulin.
Diabetes is a condition in which the body is unable to produce or use insulin effectively. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes occurs when the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough insulin.
There are several risk factors for developing diabetes, including genetics, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle. Complications of diabetes can include heart disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and blindness.
Developing a Healthy Diet Plan
A healthy diet is essential for managing diabetes. Foods that are high in fiber and low in sugar can help regulate blood sugar levels. It is important to include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your diet.
Foods to avoid include those that are high in sugar or refined carbohydrates, such as candy, soda, white bread, and pasta. Meal planning can be helpful for ensuring that you are eating a balanced diet and controlling portion sizes.
Exercising for Better Blood Sugar Control
Exercise is another important component of diabetes management. Regular physical activity can help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Types of exercise that are beneficial for people with diabetes include aerobic exercise (such as walking or cycling) and strength training.
The American Diabetes Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, spread out over at least three days. It is important to check blood sugar levels before and after exercise and to take precautions to prevent low blood sugar.
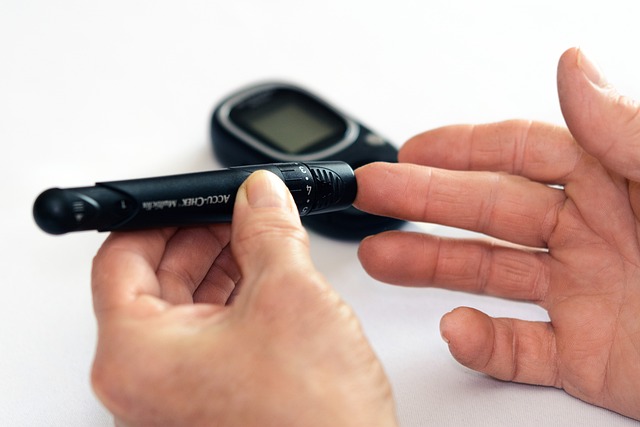
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring blood sugar levels is an essential part of diabetes management. Regular monitoring can help you identify patterns and make adjustments to your diet and medication as needed. Target blood sugar levels can vary depending on the individual and the type of diabetes.
If blood sugar levels are too high, it may be necessary to adjust medication or make changes to your diet and exercise routine. If blood sugar levels are too low, it is important to consume a source of glucose (such as fruit juice or candy) to raise them quickly.
Managing Stress and Mental Health
Stress can have a significant impact on blood sugar levels and overall health. Strategies for managing stress include exercise, relaxation techniques (such as deep breathing or meditation), and seeking support from friends and family.
Mental health is also an important aspect of diabetes management. Depression and anxiety are common among people with diabetes, and it is important to seek professional help if needed.
Working with Healthcare Providers
Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are essential for managing diabetes. Building a relationship with your healthcare team can help ensure that you are receiving the best possible care. Effective communication with healthcare providers is also important for understanding your treatment plan and making informed decisions about your health.
Staying Motivated to Live Well with Diabetes
Staying motivated can be challenging when living with a chronic condition like diabetes. Setting goals, tracking progress, celebrating successes, and finding support from friends and family can all help keep you motivated.
Living well with diabetes requires a combination of healthy lifestyle habits, regular monitoring, effective communication with healthcare providers, and support from friends and family. With the right tools and support, people with diabetes can lead long and healthy lives.