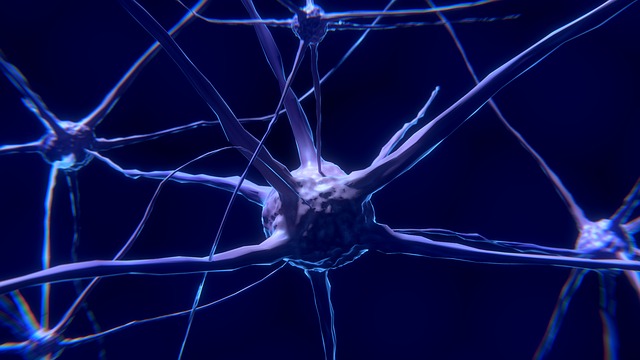
Neuropathy is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a disorder that affects the nerves and can cause a wide range of symptoms, including pain, numbness, and tingling. Neuropathy can be caused by a variety of factors, including medical conditions, injuries, and exposure to toxins. The impact of neuropathy on individuals can be significant, affecting their ability to perform daily activities and impacting their quality of life.
What is Neuropathy?
 Neuropathy is a condition that affects the nervous system. It occurs when there is damage to the nerves that transmit signals from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. This damage can cause a wide range of symptoms, including pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness.
Neuropathy is a condition that affects the nervous system. It occurs when there is damage to the nerves that transmit signals from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. This damage can cause a wide range of symptoms, including pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness.
The nervous system is responsible for controlling all of the body’s functions, including movement, sensation, and organ function. When the nerves are damaged, these functions can be disrupted, leading to a variety of symptoms.
Causes of Neuropathy
There are many different causes of neuropathy. Some common causes include diabetes, alcoholism, chemotherapy drugs, infections such as HIV or Lyme disease, and autoimmune disorders such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis.
Medical conditions such as kidney disease or liver disease can also lead to neuropathy. In some cases, neuropathy may be caused by an injury or trauma to the nerves.
Symptoms of Neuropathy
The symptoms of neuropathy can vary depending on the type of neuropathy and which nerves are affected. Common symptoms include pain or discomfort in the affected area, numbness or tingling sensations, muscle weakness or paralysis, and difficulty with coordination or balance.
In some cases, neuropathy can also cause changes in blood pressure or heart rate, digestive problems such as constipation or diarrhea, and sexual dysfunction.
Diagnosing Neuropathy
To diagnose neuropathy, doctors will typically perform a physical exam and ask about the patient’s symptoms and medical history. They may also order diagnostic tests such as nerve conduction studies, electromyography, or blood tests to help identify the underlying cause of the neuropathy.
Once the type of neuropathy has been identified, doctors can develop a treatment plan that is tailored to the patient’s specific needs.
Types of Neuropathy
There are three main types of neuropathy: peripheral neuropathy, autonomic neuropathy, and focal neuropathy.
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is the most common type of neuropathy. It occurs when there is damage to the nerves that control sensation and movement in the arms and legs. This can cause symptoms such as pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the affected areas.
Common causes of peripheral neuropathy include diabetes, alcoholism, and chemotherapy drugs. Treatment options may include medications to manage pain or improve nerve function, physical therapy to improve strength and coordination, or surgery in severe cases.
Autonomic Neuropathy
Autonomic neuropathy affects the nerves that control involuntary functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and bladder function. Symptoms may include changes in heart rate or blood pressure, digestive problems such as constipation or diarrhea, and sexual dysfunction.
Common causes of autonomic neuropathy include diabetes and autoimmune disorders. Treatment options may include medications to manage symptoms or lifestyle changes such as dietary modifications or exercise.
Focal Neuropathy
Focal neuropathy occurs when there is damage to a specific nerve or group of nerves. This can cause symptoms such as pain or weakness in a specific area of the body.
Common causes of focal neuropathy include injury or trauma to a nerve or compression of a nerve due to swelling or inflammation. Treatment options may include medications to manage pain or inflammation, physical therapy to improve strength and coordination, or surgery in severe cases.
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is the most common type of neuropathy. It occurs when there is damage to the nerves that control sensation and movement in the arms and legs. Common causes of peripheral neuropathy include diabetes, alcoholism, and chemotherapy drugs.
Symptoms of peripheral neuropathy may include pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the affected areas. Treatment options may include medications to manage pain or improve nerve function, physical therapy to improve strength and coordination, or surgery in severe cases.
Autonomic Neuropathy
Autonomic neuropathy affects the nerves that control involuntary functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and bladder function. Symptoms may include changes in heart rate or blood pressure, digestive problems such as constipation or diarrhea, and sexual dysfunction.
Common causes of autonomic neuropathy include diabetes and autoimmune disorders. Treatment options may include medications to manage symptoms or lifestyle changes such as dietary modifications or exercise.
Focal Neuropathy
Focal neuropathy occurs when there is damage to a specific nerve or group of nerves. This can cause symptoms such as pain or weakness in a specific area of the body.
Common causes of focal neuropathy include injury or trauma to a nerve or compression of a nerve due to swelling or inflammation. Treatment options may include medications to manage pain or inflammation, physical therapy to improve strength and coordination, or surgery in severe cases.
Treating Neuropathy
Treatment for neuropathy will depend on the type of neuropathy and the underlying cause. In some cases, treating the underlying medical condition may help improve symptoms of neuropathy.
Medications such as pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and antidepressants may be used to manage symptoms of neuropathy. Physical therapy can also be helpful in improving strength and coordination.
Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine can also help manage symptoms of neuropathy.
Neuropathy is a condition that can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life. It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you may have neuropathy, as early diagnosis and treatment can help improve symptoms and prevent further damage to the nerves.
There are many different types of neuropathy, each with its own set of symptoms and treatment options. By working with your healthcare provider, you can develop a treatment plan that is tailored to your specific needs and helps you manage your symptoms effectively.